Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, businesses frequently use multiple domains or subdomains to engage users and offer specialized experiences. Tracking users across these domains, however, can be challenging. How to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager is a critical task to ensure accurate tracking across different properties. Google Tag Manager (GTM) provides a seamless solution for configuring domains to enable accurate tracking and holistic insights. Whether you’re managing a single domain or multiple, knowing how to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager can significantly improve your data tracking accuracy. This guide will walk you through the steps for setting up cross-domain tracking in GTM, covering all essential details and potential roadblocks.Plus, we’ll highlight ways to enhance your site’s overall tracking, with recommendations on Website Maintenance Services and Google Analytics Consulting Services for added support.
What Is Cross-Domain Tracking and Why Is It Important?
With cross-domain tracking, a website owner can track the activity of a user across multiple domains as a single session, providing a much more accurate understanding of customer behavior. Even when navigating from one domain to another, GTM will still track them and won’t split data into separate sessions. This offers unified data that is invaluable for businesses such as eCommerce platforms, SaaS providers, and content sites—especially when they operate under different domains.
For instance, an online eCommerce business may have one domain for its online store and another for its blog. Knowing how to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager properly will give you an all-rounded picture of the user journey across both domains. By understanding how to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager effectively, businesses can ensure that user actions on different sites are correctly attributed to the same session, improving the accuracy of their funnel analysis. According to The Gray Company, how to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager and set up cross-domain tracking ensures that activities across different domains are appropriately tracked, offering a clear view of user interactions across your entire digital ecosystem.
Step 1: Setting Up Google Analytics for Cross-Domain Tracking
The first step in configuring cross-domain tracking is setting up Google Analytics (GA) to recognize and manage user sessions across domains. This requires some backend adjustments, particularly in Google Analytics Consulting Services, as each property needs to be aligned with your GTM configuration.
- Open Google Analytics and navigate to Admin Settings.
- Under Property, select Tracking Info, then click Referral Exclusion List.
- Add your domains to the exclusion list. This prevents GA from counting traffic between your domains as a referral, allowing seamless session tracking.
Tip: For optimal performance, use Universal Analytics (UA) or GA4, depending on your website setup. UA works well with traditional setups, but GA4 is preferable for users who want more flexibility in tracking events.
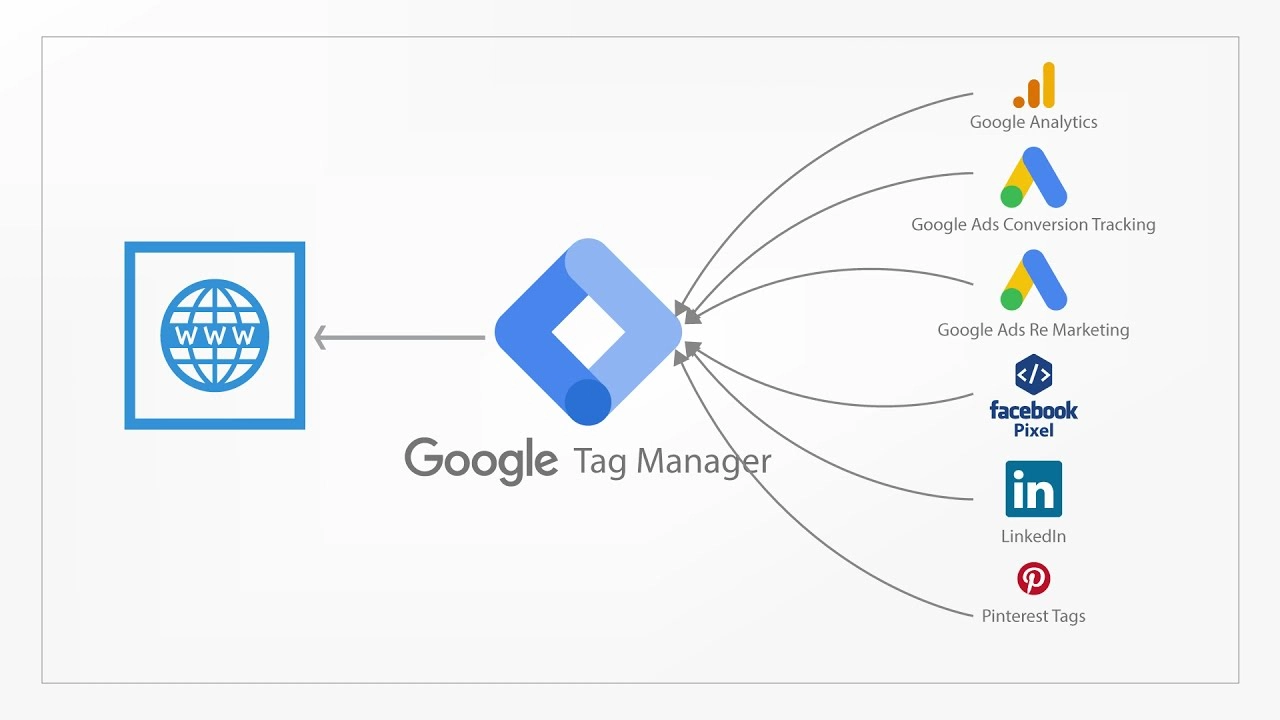
Step 2: Configuring Google Tag Manager for Cross-Domain Tracking
In this step, you’ll set up GTM to recognize and manage user data across domains by linking tags and triggers across your sites.
1. Add the GTM Container to Each Domain: Make sure each domain has the same GTM container. If your domains are set up through different CMS platforms, such as WordPress or Shopify, consider using WordPress Development Services or Shopify Maintenance Services to ensure accurate deployment.
2. Update the Tag Settings:
- Open Google Tag Manager and go to Tags.
- Select the GA tag you’ll be using for cross-domain tracking. Click Tag Configuration > More Settings > Fields to Set.
- In the field, enter allowLinker with the value set to true.
- Next, scroll to Cross Domain Tracking and add your domains under Auto Link Domains.
3. Modify Triggers and Variables:
- Create a trigger that captures clicks between your primary domain and linked domains.
- Add a URL Variable to track the user’s origin domain, which helps to differentiate user actions across sites.
For assistance, consult a B2B Web Design Agency to set up and test GTM if you’re managing complex cross-domain needs
Also Read: What Are The Five Sections of The Google Analytics Dashboard
Step 3: Testing Your Cross-Domain Configuration
Testing is crucial for verifying that the configuration is working as intended. Inaccuracies in cross-domain tracking can lead to data inconsistencies that affect your marketing insights and decision-making.
1. Use Google Tag Assistant: Google’s Tag Assistant Chrome extension is a useful tool for checking if GTM is working across domains.
2. Verify Tracking in Real-Time Reports: Open Google Analytics in a separate tab and monitor Real-Time reports. Click through your links to see if the user activity is logged accurately as a single session across domains.
If you run into issues, consult Google Tag Management Consulting Services for expert troubleshooting.
Step 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid in Cross-Domain Tracking Setup
Cross-domain tracking can be complex, and there are several common mistakes that can disrupt your setup. Avoid these issues to ensure smooth tracking across your domains:
- Not Adding All Domains: Ensure every domain is accounted for in the GTM container, as even one missing domain can fragment data.
- Incorrectly Configured Auto Link Domains: Make sure the domains listed in the Auto Link Domains field match exactly. A typo can lead to incorrect data tracking.
- Skipping Referral Exclusion Setup: Referral exclusions are critical for GA to interpret inter-domain navigation correctly.
Consider Website Redesign Services if you find that technical limitations or structural issues hinder your setup. Redesigning specific aspects of your site could streamline cross-domain tracking implementation.
Advanced Configurations in Google Tag Manager for Cross-Domain Tracking
Once you’ve established basic tracking, advanced configurations can enhance insights. Here are a few options to consider:
- Track Subdomains Separately: If you’re managing subdomains, you can specify them in Auto Link Domains to track user behavior distinctively on each one.
- Add Event Tracking: Set up event tracking to capture detailed interactions, like button clicks, file downloads, or form submissions across domains.
- Custom Dimensions: Configure custom dimensions in GTM to track more specific user actions, like login events or purchases.
These advanced techniques provide richer data and may require assistance from Responsive Website Development Services to ensure compatibility across devices.
Benefits of Cross-Domain Tracking for Business Insights
Cross-domain tracking provides substantial business insights by consolidating user data across multiple platforms, which can lead to better marketing, customer service, and website design. Here are some ways it benefits businesses:
- Enhanced User Journey Insights: Knowing where users navigate between domains can inform product positioning and content strategy.
- Accurate Conversion Data: With cross-domain tracking, conversions initiated on one domain but completed on another are accurately attributed.
- Improved Marketing ROI: By understanding the full user journey, you can make data-driven adjustments to marketing campaigns, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Also Read: What Better Google Analytics or Yandex Metrics
Using Cross-Domain Tracking Data to Improve User Experience
The data gathered from cross-domain tracking can be used to improve the user experience by identifying pain points and optimizing content.
- Identify Drop-Off Points: If users frequently leave your site after moving between domains, consider redesigning those pages.
- Optimize for Seamless Navigation: Adjust linking structures and CTAs to ensure smooth transitions, reducing bounce rates.
- Create a Cohesive Brand Experience: Consistent branding and navigation help users feel connected to your content across domains.
Life counseling services are metaphorically similar, as they offer guidance and structure across life areas. Similarly, a holistic approach to web tracking unifies the user experience across touchpoints.
Conclusion
Configuring cross-domain tracking in Google Tag Manager is essential for businesses managing multiple websites. How to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager is a critical step in achieving unified data, accurate user journey insights, and better conversion tracking. Although setting up cross-domain tracking requires careful planning and technical configuration, understanding how to configure your domains in Google Tag Manager can simplify the process and provide the improved insights you need. Leveraging unique website visitors google analytics average cost of website design for small business Google Analytics Consulting Services or a B2B Web Design Agency can make this process smoother, ensuring your data collection is reliable and actionable. This knowledge helps businesses track users across different domains and ensures a more seamless digital experience.
Also Read: Add The Google Analytics Code To Your Canva Website
FAQ’s
How do I change my domain in Tag Manager?
To update to the new endpoint:
- Save and go back to your workspace.
- Open Google Tag Manager.
- Open the server container that is set up on the same origin as the website.
- Under Admin tab > Container Settings, remove all previous URLs. …
- Click Add URL and input your the URL including the path prefix.
How to configure Google Tag Manager?
Step 1: Create a Google tag
- Open Google Tag Manager.
- Select the container you want to configure. Open the Tags menu.
- Create a New tag. …
- In the Tag Configuration box, select Google tag.
- Optional: You can set up additional configuration options to govern how your Google tag communicates with its destinations.
What is a GTM domain name?
A GTM domain is a DNS domain, whose name usually ends in . akadns.net. These additional namespaces are also present: akadns6.net and akadns99.net. The namespace akadns6.net is currently not in use.





Leave a Reply